The Difference Between Congenital Limb Difference and Amputation
When it comes to limb differences, it's crucial to distinguish between congenital limb difference and amputation. While both conditions result in the absence of a limb, their origins, implications, and treatments vary significantly. Understanding these differences can provide valuable insights for those affected and their loved ones.

What is Congenital Limb Difference?
Congenital limb difference refers to limb abnormalities present at birth. These can manifest as missing or underdeveloped limbs. Several factors contribute to congenital limb differences, including:
Congenital limb difference refers to limb abnormalities present at birth. These can manifest as missing or underdeveloped limbs. Several factors contribute to congenital limb differences, including:
Genetic Factors: Mutations or inherited conditions can cause limb differences.
Environmental Influences: Exposure to certain medications, chemicals, or infections during pregnancy can impact limb development.
Vascular Issues: Problems with blood flow during fetal development can lead to limb malformations.

What is Amputation?
Amputation involves the surgical removal of a limb due to injury, disease, or other medical conditions. Common causes include:
Amputation involves the surgical removal of a limb due to injury, disease, or other medical conditions. Common causes include:
Trauma: Severe injuries from accidents or combat can necessitate amputation.
Medical Conditions: Diseases like diabetes, cancer, and severe infections can lead to limb removal.
Circulatory Problems: Poor blood flow, often associated with conditions like peripheral artery disease, can result in tissue death, requiring amputation.
Differences in Treatment and Rehabilitation
The treatment approaches for congenital limb differences and amputations differ, reflecting their distinct origins:
Congenital Limb Difference Treatment
Early Intervention: Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial. Pediatric specialists, including orthopedic surgeons and physical therapists, work together to develop a treatment plan.
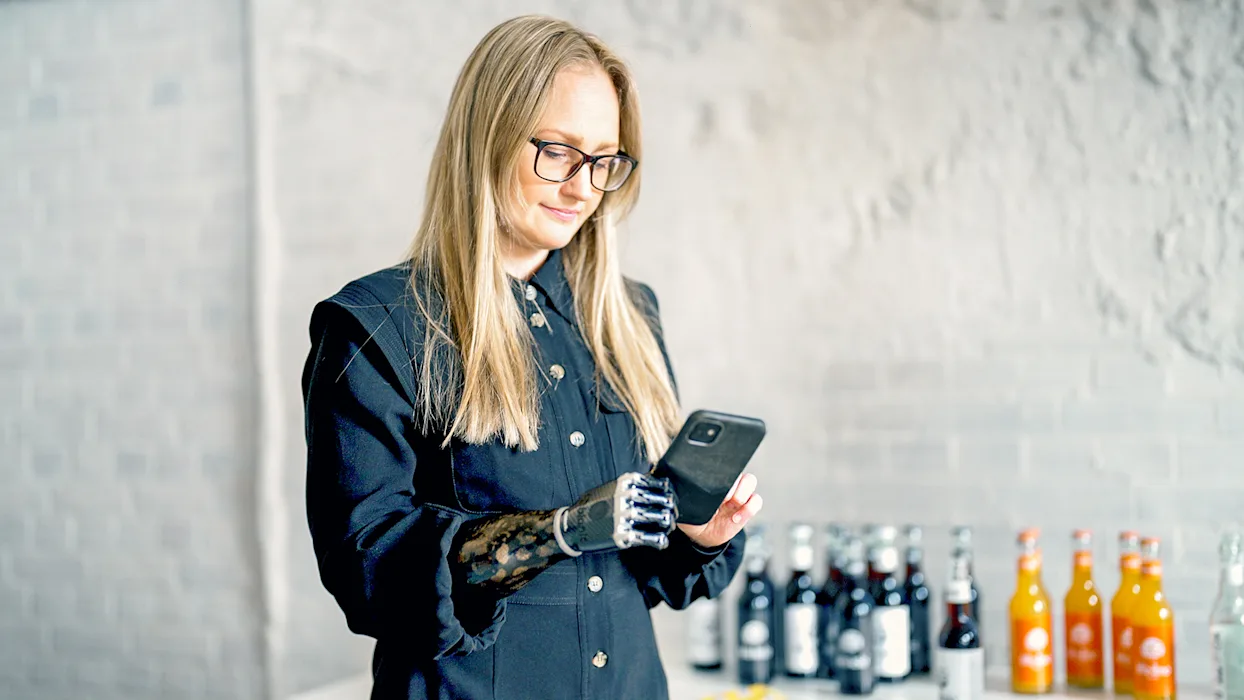
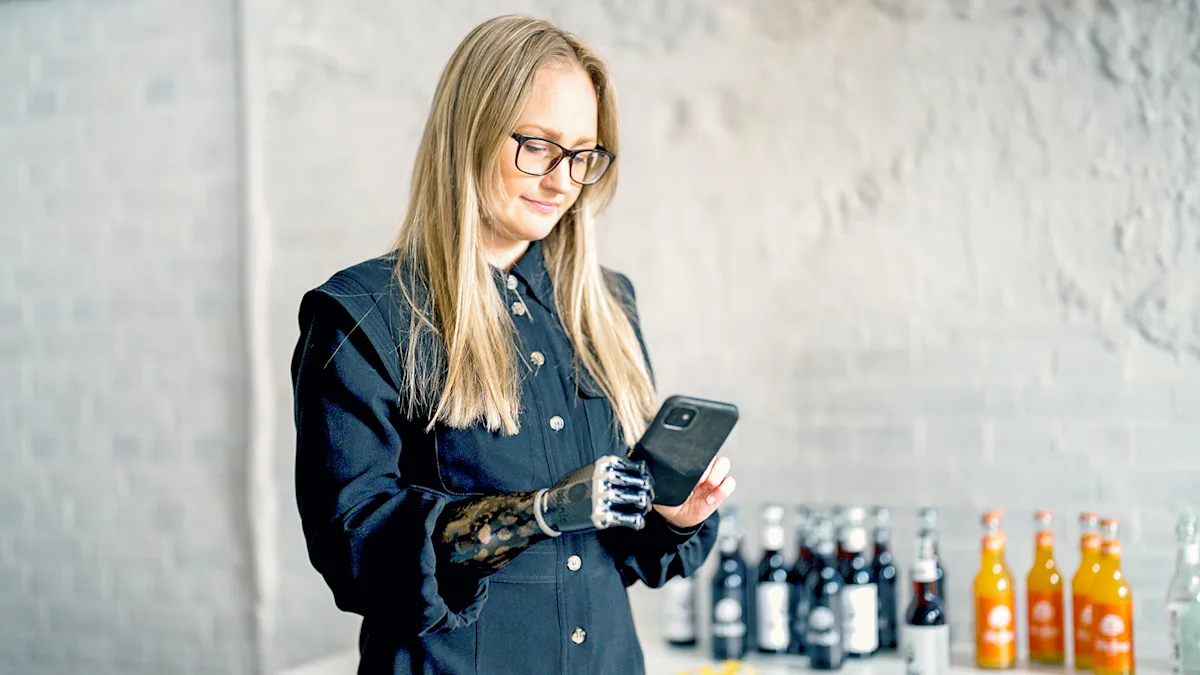
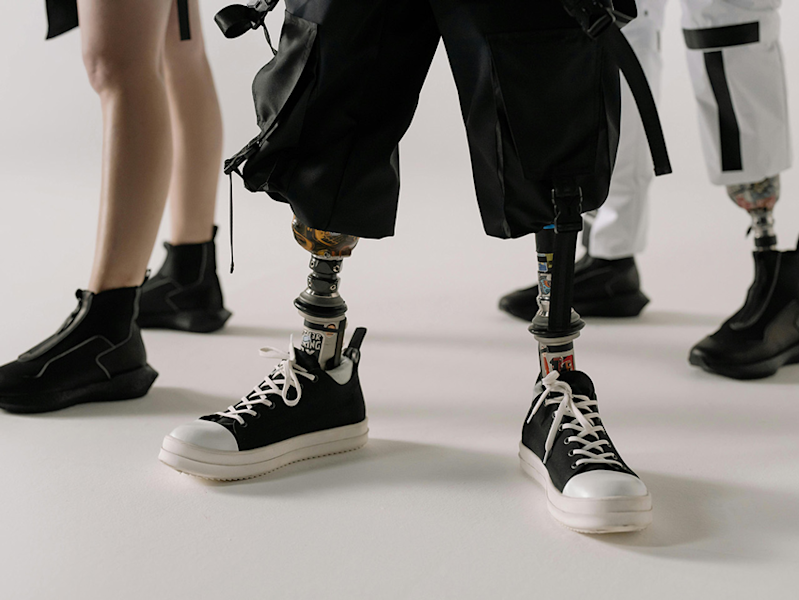
Prosthetics: Children with congenital limb differences often benefit from prosthetics fitted early in life, with adjustments made as they grow.
Therapy: Occupational and physical therapy help children adapt and develop motor skills.
Amputation Treatment
Surgical Care: Amputation surgery requires careful planning to ensure proper healing and prepare the residual limb for a prosthetic.
Prosthetics: Similar to congenital limb differences, amputees receive prosthetic limbs, tailored to their needs and lifestyle.
Rehabilitation: Post-amputation rehabilitation includes physical therapy, pain management, and psychological support to aid in the adjustment process.
Psychological and Social Considerations
Both congenital limb differences and amputations have profound psychological and social impacts:
Congenital Limb Difference: Children may face challenges in social integration and self-esteem. Supportive family environments and early socialization can mitigate these effects.
Amputation: Adults may experience grief, depression, and identity issues following limb loss. Counseling and peer support groups play vital roles in recovery.
Understanding the difference between congenital limb difference and amputation is essential for providing appropriate care and support. While congenital limb differences are present at birth and often involve genetic or environmental factors, amputations result from injuries or medical conditions. Both require specialized treatment and rehabilitation to ensure the best possible outcomes for those affected.
If you or a loved one is dealing with limb difference, seeking guidance from healthcare professionals specializing in these areas can make a significant difference in quality of life and overall well-being.
Get a Consultation
Are you ready to take the next step towards improved mobility and comfort? Find an orthotics and prosthetics clinic near you and schedule your appointment today!